Ubiquinone, more commonly known as CoQ10, is an organic compound that the body produces naturally. It plays a critical role in energy production and can be located in high concentrations within the heart, liver, and kidney. Acting as an antioxidant it guards cells against free radicals which are detrimental molecules that cause harm to cellular structures.
- Extensive research has been conducted on CoQ10’s capacity to improve various aspects of health, including cardiovascular well-being, neurological conditions, and cancer. Noteworthy studies have found that taking this supplement can reduce blood pressure levels, enhance symptoms associated with heart failure, counter muscle damage caused by statins used for cholesterol management as well as better Parkinson’s disease-related signs.
- Research has indicated that CoQ10 may potentially be effective in preventing cancer through the improvement of chemotherapy agents, and decreasing the growth rate of cancerous cells. Additionally, it is thought to reduce many common side effects related to cancer treatment including fatigue, muscle weakness, and high cholesterol levels.
- Although more research is needed to fully determine the potential health benefits of CoQ10, current studies have yielded encouraging results. When considering CoQ10 as a supplement for your wellness plan, it’s essential to speak with your healthcare professional first - even though CoQ10 is generally safe for use by most people.
This article will investigate the potential effect of CoQ10 supplements on estrogen levels in the body. The main inquiry is whether taking CoQ10 can heighten or lower a person’s estrogen level. Although it must be stated that there isn’t any substantial evidence to prove a direct relationship between these two, some studies have suggested an association between them.
What is CoQ10 and how does it work in the body?
Ubiquinone, or CoQ10, is a naturally-occurring compound that our bodies need to generate energy. Extensive amounts of this essential nutrient are found in the heart, liver, and kidneys.
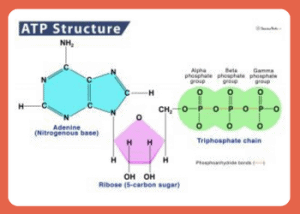 CoQ10 is fundamental in the synthesis of adenosine triphosphate (ATP), which is a critical source of energy for cells. Furthermore, it serves as an imperative antioxidant that preserves and safeguards cells from detrimental free radicals.
CoQ10 is fundamental in the synthesis of adenosine triphosphate (ATP), which is a critical source of energy for cells. Furthermore, it serves as an imperative antioxidant that preserves and safeguards cells from detrimental free radicals.
As we get older, our bodies naturally create fewer CoQ10 levels. Similarly, certain medical conditions and medications such as statins can further decrease CoQ10 production in the body.
Considering these factors, using a supplement to increase your CoQ10 intake has been touted as an efficient way of enhancing cardiovascular health, and improving symptoms associated with neurodegenerative diseases and cancer.
CoQ10 exists as capsules, tablets, and creams in addition to being found in trace amounts of fatty fish, organ meats, and whole grains - all readily available ingredients.
This article will delve into available scientific studies to ascertain the correlation between CoQ10 and estrogen levels. We’ll evaluate these study results, analyze potential mechanisms that might link them together, and then provide a conclusion based on our findings.
What is estrogen and how does it work in the body?
Estrogen is an essential hormone for proper reproductive and sexual development in both females and males. Females primarily produce estrogen from their ovaries, while the testes are responsible for creating it within males. Small amounts of this vital hormone can also be found in one’s adrenal glands as well as fat cells.
| Males | Females |
|---|---|
| Produce estrogen in the testes | Produce estrogen primarily in the ovaries |
| Estrogen helps maintain bone density | Estrogen helps maintain bone density |
| Estrogen helps regulate mood and sex drive | Estrogen helps regulate the menstrual cycle and pregnancy |
| Estrogen helps control the growth of prostate cells | Estrogen helps develop secondary sexual characteristics |
| High levels of estrogen can lead to feminization | High levels of estrogen can lead to an increased risk of certain types of cancer such as endometrial and breast cancer |
| High levels of estrogen can lead to decreased sex drive | High levels of estrogen can lead to menstrual irregularities and weight gain |
- Estrogen is essential for the development of women’s secondary sexual characteristics, such as breast growth and regulation of the menstrual cycle.
- Estrogen also helps in keeping bones strong and healthy, as well as decreases cholesterol levels.
- Estrogen is also produced in males and plays a role in keeping bones strong, maintaining cardiovascular health, stabilizing mood and sex drive, and restraining prostate cell growth.
- Normal levels of estrogen are important for sexual health and function, but excessive or deficient levels can result in serious medical issues.
- Excessive amounts of estrogen in women can increase the risk of endometrial and breast cancer, while in men it can cause feminization, enlarged breasts, reduced libido, and sterility.
- The connection between estrogen levels and health is complex and not fully understood, but maintaining healthy levels of estrogen within a normal physiological range is essential for overall well-being.
- Estrogen is an essential hormone for female reproductive and sexual health, as it helps in the development of secondary characteristics, regulates menstrual cycles, and thickens the uterine lining in anticipation of conception.
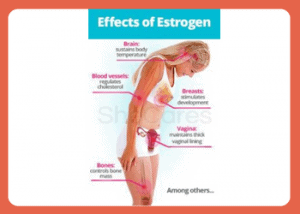 During the menstrual cycle, estrogen levels ebb and flow with an apex during ovulation. During this surge in estrogen, the ovaries release an egg, and should fertilization occur; these high levels of the hormone will maintain to nourish a pregnancy.
During the menstrual cycle, estrogen levels ebb and flow with an apex during ovulation. During this surge in estrogen, the ovaries release an egg, and should fertilization occur; these high levels of the hormone will maintain to nourish a pregnancy.
On the other hand, if fertilization does not take place then the endometrium is shed as estrogens drop causing menstruation.
Estrogen is essential for the development and maintenance of a healthy vaginal epithelium, allowing it to remain lubricated. Moreover, estrogen works to reduce the likelihood of urinary tract infections by keeping your urinary tract in optimal condition.
Although not as prominent as testosterone in males, estrogen still plays an important role in overall sexual health; helping sustain erectile function, sex drive, and sperm production!
- The body requires a certain amount of estrogen for optimal function, but too much or too little can lead to health complications.
- Estrogen dominance, or an excess of estrogen in a woman’s system, can increase the risk of endometrial cancer and breast cancer.
- An imbalance of estrogen and progesterone can also increase the risk of endometrial cancer.
- For men, an excessive amount of estrogen can contribute to the development of prostate cancer, as well as other effects such as breast enlargement, reduced libido, and infertility.
- Estrogen imbalance can also cause other health issues including menstrual irregularities, weight gain, depression, and a heightened danger of blood clots.
- It is important to maintain healthy levels of estrogen within the normal physiological range for overall well-being.
- If you suspect that your estrogen levels are out of balance or if you’re experiencing any symptoms related to a hormonal imbalance, it’s best to seek advice from a healthcare expert.
Furthermore, Vitamin D is essential for maintaining healthy bones, stabilizing mood swings, and preventing the overgrowth of prostate cells.
As both men and women age, their levels of estrogen will steadily drop as a result of menopause or andropause. As these hormones decrease, so do sexual functioning and fertility. Unfortunately, this can also lead to an elevation in the odds of diseases such as osteoporosis.
The current research on CoQ10 and Estrogen
Although the correlation between CoQ10 and estrogen levels is still unclear, there have been a few studies conducted on this topic with inconclusive findings. It remains to be seen whether taking supplemental CoQ10 can actually affect estrogen production in one’s body.
Recent research has indicated that CoQ10 supplements may be beneficial in regard to estrogen levels. In one study, rats who were administered the supplement experienced an uptick in their estrogen concentrations as well as a heightened bone density.
 In a study of postmenopausal women, CoQ10 supplementation was linked to an increment in circulating estrogen levels and a reduction in FSH and LH hormone concentrations. These hormones are closely correlated with the menstrual cycle.
In a study of postmenopausal women, CoQ10 supplementation was linked to an increment in circulating estrogen levels and a reduction in FSH and LH hormone concentrations. These hormones are closely correlated with the menstrual cycle.
On the other hand, some studies have determined that CoQ10 supplementation makes no meaningful difference in estrogen levels. For example, a study of postmenopausal women found absolutely no differences in their estrogen levels whether they took CoQ10 supplements or not.
Numerous studies have sought to explain how CoQ10 could potentially influence estrogen levels. According to the findings, it appears that CoQ10 might alter certain enzymes associated with estrogen metabolism and genes connected with its formulation. Nevertheless, our comprehension of these mechanisms is still in its developmental stage; additional research must be conducted to further understand this relationship.
It’s imperative that we understand the full scope of the relationship between CoQ10 and estrogen before making any decisions about supplementing with either. While research is still limited, it does not offer a definitive answer as to whether or not taking CoQ10 will raise or lower your levels of estrogen. It would be wise for you to speak with your healthcare provider prior to adding any supplements into your routine, particularly if you are on hormone therapy or have an elevated risk factor for certain imbalances caused by hormones.
Results from our inquiry exploring the correlation between CoQ10 and estrogen levels have revealed:
- Research has suggested that CoQ10 supplementation may result in an elevation of estrogen levels. In one rat study, researchers observed a boost in both the hormone and bone density following CoQ10 supplements. Furthermore, a different postmenopausal women experiment indicated that such supplements were correlated with heightened estrogen levels and decreased FSH/LH hormones associated with menstruation.
- On the other hand, assorted studies have revealed that CoQ10 supplementation had no noteworthy effect on estrogen levels. Research conducted in postmenopausal women is a primary example of this; it discovered no substantial alteration in estrogen concentrations between the group given CoQ10 supplements and those who weren’t.
- Research has suggested that CoQ10 may have the potential to regulate hormones, especially estrogen metabolism. This implies a relation between CoQ10 supplementation and altered levels of estrogen in humans.
- Results from past research have hypothesized that CoQ10 may affect the genetic coding of estrogen production and account for how supplementing with CoQ10 could alter levels of estrogen.
- Although CoQ10 is linked to estrogen levels, researchers have yet to fully comprehend the intricacies of this relationship. To gain a better understanding, further research must be conducted in order to confirm existing conclusions.
It’s essential to remember that while certain studies have established a relationship between CoQ10 and estrogen levels, they have not proven causation. Thus it is vital to wait for more research before drawing any meaningful conclusions about this correlation.
Conclusion
When considering the use of CoQ10 supplements, it is essential to consider a person’s health status, current medications, and potential interactions with other compounds. However, although there are some promising research results about CoQ10 and estrogen levels existing today; a further exploration into this topic is required to have a clear understanding of these substances.
Research has long been conducted to uncover the many benefits associated with CoQ10 and its impact on a variety of health conditions, including heart disease and skin aging. Estrogen’s contribution to healthy skin is well known as it assists in keeping collagen levels steady and maintaining moisture balance. Further studies are indicating that when combined, these two elements may create a synergistic effect which could potentially increase elasticity while diminishing the appearance of wrinkles and fine lines for an improved complexion!
