This article serves to thoroughly compare two prominent anti-aging supplements: nicotinamide riboside (NR) and nicotinamide mononucleotide (NMN). With the aim of elucidating similarities and differences between NR versus NMN, this article seeks to assist readers in selecting which supplement is most advantageous for their personal well-being.
After a comprehensive investigation into the background, progress, and probable health advantages of both supplements, this article is here to help readers make an informed choice about which supplement satisfies their needs. The facts provided will aid them in making the best decision for themselves.
Table of Contents
What are Nmn Supplements?
Nicotinamide mononucleotide (NMN) is a unique nucleotide supplement that contains nicotinamide, an extraordinary form of vitamin B3. Additionally, it also consists of one single mononucleotide molecule; thereby combining the potency of both vitamins and molecules for amazing health benefits!
NMN is taking the world of anti-aging supplements by storm due to its remarkable ability to raise energy, promote metabolic efficiency and enhance cellular function.
It acts as a forerunner for nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+), an essential molecule that plays a critical role in energy metabolism and restoring cells’ integrity. Therefore, NMN has been considered one of the most promising nutritional tools for slowing down aging processes.
What is NR Supplement?
Nicotinamide riboside (NR) is an advantageous form of vitamin B3 that has recently been credited for its potential anti-aging properties. When consumed, NR works to generate the immensely valuable molecule known as nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+).
Meaningful in a variety of cell activities such as energy metabolism, DNA repair, and cellular signaling – NAD+ can make all the difference when it comes to preserving youth!
Is NR the key to unlocking a more youthful, energetic you? Research suggests that higher amounts of NAD+ may result in improved energy metabolism and overall better cellular function, possibly decreasing age-related decline.
Additional studies have highlighted potential positive effects on metabolism and stamina from taking NR supplements – all while promoting healthy aging. If you’re looking for something to give you an edge against time’s cruel march forward, then consider adding some NR into your daily routine.
Similarities Between NR and NMN
Nicotinamide Riboside (NR) and Nicotinamide Mononucleotide (NMN) are both supplements that belong to the NAD precursors family. You may be wondering, what is NAD? It stands for Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide – an essential coenzyme found in all living cells playing a key role in energy metabolism DNA repair and cellular signaling.
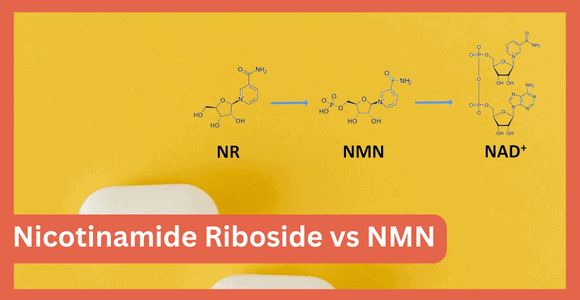
While both NR and NMN share a similar structure, it’s important to note that NMN acts as a direct precursor of NAD while NR has one more step in its conversion process into the same compound.
NR and NMN are both supplements that work by restoring NAD levels in the body, which activate enzymes responsible for various cellular processes. Due to diminishing quantities of NAD as we age, these two substances may help replenish our natural supplies and improve cell health.
The potential benefits of NR/NMN include increased energy metabolism, improved DNA repair capabilities, heightened cellular communications, and reduced oxidative damage from free radicals – all factors leading to enhanced cognitive function, better cardiovascular performance & eye health plus anti-aging effects.
When it comes to NR and NMN supplements, the suggested dosages range from 250-1000 mg per day depending on an individual’s desired goals. Although this is generally true, we always suggest talking to a healthcare provider prior to taking any new supplement in order to determine what amount would be safest and most suitable for you!
Consequently, NR and NMN are comparable supplements that boost NAD levels in the body. Both have indicated potential health advantages; however, further research is needed to gain a comprehensive understanding of their effects and come up with secure dosage guidelines.
Differences Between NR and NMNFrequently Asked Questions
Here is a summary of the differences:
Chemical Structure:
- NR is a form of Vitamin B3 (niacin) and has a ribose sugar molecule attached to the nicotinamide molecule.
- NMN is a nucleotide, which is a building block of DNA and has a different chemical structure than NR.
Metabolism:
- NR is converted into NMN in the body before being converted into NAD.
- NMN is directly converted into NAD, bypassing the conversion step from NR.
Health Benefits:
- Both NR and NMN have been shown to have anti-aging effects and improve energy metabolism.
- However, NMN has been found to be more effective in increasing NAD levels, which may lead to greater health benefits.
- NR has also been shown to have positive effects on glucose metabolism and may have potential benefits for Type 2 Diabetes.
Dosages:
- Recommended dosages for NR range from 250-1000 mg per day.
- Recommended dosages for NMN range from 500-2000 mg per day.
It’s important to note that more research is needed to establish safe and effective dosing recommendations for both supplements.
In conclusion, NR and NMN are similar supplements, but they have different chemical structures, metabolize differently in the body, and may offer different health benefits. It’s important to consult with a healthcare professional before taking either supplement to determine the right dose for you.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Kind of NMN does David Sinclair Use?
While he does not explicitly suggest any NNM companies, Sinclair has endorsed GMP NMN as a reliable option. Sinclair is renowned for his research on aging and his striving to mitigate its effects.
Should I Take NMN and NAD+?
Supplementing with NMN, alongside NAD, is a much more direct and quicker way to maximize cell metabolism. Not only has it been found to boost insulin activity for additional metabolic advantages, but also improves sugar tolerance levels.
How Much Nicotinamide Riboside or Nicotinamide Mononucleotide Should I Take for the Best Results?
Most studies conducted so far have used doses ranging from 100-500 mg of NR and 100-250 mg of NMN, although some research has used higher doses up to 1,000 mg.
The optimal dose may vary depending on factors such as age, health status, and individual response, so it’s important to speak with a healthcare provider before starting any supplement regimen.
What’s The Difference Between Tru Niagen And NMN?
Tru Niagen and NMN (Nicotinamide Mononucleotide) are both dietary supplements that aim to boost nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+) levels in the body, a coenzyme essential for various biological processes, particularly those related to energy metabolism and cellular repair. However, they differ in their chemical composition, mechanism of action, and regulatory status.
- Composition:
- Tru Niagen: Tru Niagen is a brand of nicotinamide riboside (NR), which is a precursor to NAD+. NR is converted into NAD+ through a series of enzymatic reactions in the body.
- NMN (Nicotinamide Mononucleotide): NMN is another precursor to NAD+ but has a slightly different chemical structure. NMN is directly converted into NAD+ through a single enzymatic step by the enzyme NMN adenylyltransferase (NMNAT).
- Mechanism of Action:
- Tru Niagen: NR, found in Tru Niagen, is converted into NMN within the body and then further metabolized into NAD+. This multi-step process regulates the rate at which NAD+ is replenished.
- NMN: NMN, being more proximal to NAD+ in the metabolic pathway, has the advantage of more direct conversion to NAD+. This potentially makes NMN a more efficient NAD+ precursor.
- Research and Efficacy:
- Both Tru Niagen and NMN have gained attention for their potential anti-aging and health-promoting effects. Some studies suggest that increasing NAD+ levels through NR or NMN supplementation may positively impact various cellular processes, including DNA repair and sirtuin activation, which are associated with aging and age-related diseases.
- Regulatory Status:
- Tru Niagen, containing NR, has received Generally Recognized as Safe (GRAS) status from the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA), indicating it is considered safe for consumption.
- NMN is still under investigation and does not have the same level of regulatory approval. It is available as a dietary supplement but has not undergone the same rigorous safety assessments as Tru Niagen.
- Cost and Availability:
- Tru Niagen is a commercial product available in various forms and is widely accessible.
- NMN is also available as a supplement but may have varying sources and purities, which can affect its cost and quality.
In conclusion, both Tru Niagen and NMN aim to boost NAD+ levels, potentially offering health benefits, although the exact differences in efficacy remain an active area of research. Tru Niagen contains NR and has received FDA approval, making it a more established option. NMN, on the other hand, is more directly converted to NAD+ but lacks the same level of regulatory approval. As with any dietary supplement, it’s essential to consult with a healthcare professional before use, especially given the ongoing research into these compounds and their effects on health and aging.
Conclusion. Which is Better NMN or Nicotinamide Riboside?
The question of which supplement is best for anti-aging, NR (Nicotinamide Riboside) or NMN (Nicotinamide Mononucleotide), is still the subject of ongoing research. Both supplements have been shown to have anti-aging effects and increase NAD levels in the body, which is important for cellular processes that impact aging.
Studies have shown that NMN is more effective in increasing NAD levels than NR, but NR has also been found to have positive effects on glucose metabolism and may have potential benefits for Type 2 Diabetes. Additionally, the recommended dosages for NR are lower than those for NMN, which may make it a better choice for some individuals.
While both NR and NMN have shown promising results in anti-aging research, more research is needed to fully understand their effects and establish safe and effective dosing recommendations.
In conclusion, both NR and NMN show potential as anti-aging supplements, and the best choice will depend on an individual’s specific needs and goals. It’s important to consult with a healthcare professional before taking any new supplement to determine the right dose for you.